
The code in the image defines two classes, A and B. Class A has a show method that simply prints “A”. Class B inherits from class A and overrides the show method to print “B”. The code then creates an object of type B and calls its show method. Since the show method in class B is the one that is actually executed, the output will be “B”.

Since maxVal is initialized to a value that is greater than all values in arr, maxVal will never be updated and 0 will be returned. To correct this, maxVal should be initialized to the first element in arr or initialized to Integer.MIN_VALUE.

The method should return false since the word “art” is not found in “rattrap”, “similar”, or “today”. When the method concatenates all three words together, all is assigned the value “rattrapsimilartoday”. The “ar” in “similar” gets concatenated with the “t” in “today”, resulting in the letter combinations for “art” to be in all, causing the method to incorrectly return true.

The outer loop iterates six times for when outer is assigned the values 1 through 6. For each iteration, the number of times the inner loop iterates is dependent on the value of outer.

result[2] is assigned the value 3. The final iteration of the for loop, when j is 3, result[3] is assigned the product of row 1, column 3, which is 4, and row 3, column 2, which is 1. Therefore, result[3] is assigned the value 4.

I forgot to account that ! sign also applied to the variables and not only the signs. Therefor it should always be false no matter what

The boolean expression ((a > b) && (a > c)) would be false because a is not greater than b, so the code will evaluate the boolean expression in the else if. The boolean expression ((b > a) && (b > c)) will also evaluate to false because b is not greater than a, this will cause c to be returned, however c is the smallest of the three integers and not the greatest.

The loop will stop iterating when loop has the value num + 2 So it should be the sum of all odd numbers from 1 and whatever num is inclusive
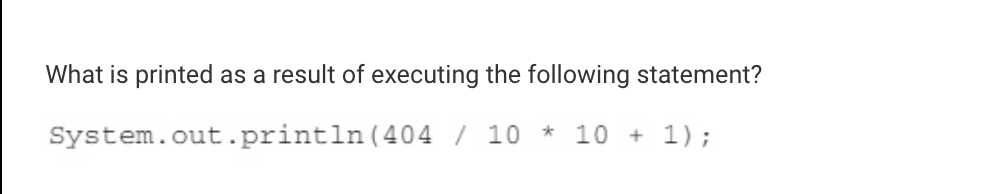
Correct. The first operation that is executed is 404 / 10. Since both 404 and 10 are integers, integer division is used resulting in 40. The value 40 is then multiplied by 10, resulting in 400, and finally 1 is added, meaning 401 is printed.

Choice 1 would have a compiler error because it has the same method signature. Choice II can be added to the SomeMethods class because, although it has the same name (one), the parameter list has the types String, int which has a different order than the method public void one (int first, String second). Choice III can be added to the SomeMethods class because there are three int parameters and no other method named one has three int parameters.

4 is the value of count after the first iteration of the outer loop. In the fourth and final iteration of the outer loop, the inner loop will iterate one time (for y = 3) and count will be 10.

The answer I selected would be the result if we were finding the largest element instead of the smallest element and moving it into its proper sorted position.

Choice I sets max to Integer.MIN_VALUE, which is the smallest possible integer value. Then it accesses each element in arr and assigns them value. If value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far. Choice II uses an if statement inside the for loop to check and see if value is the first element in arr or not. Once the first element is identified, max is initialized to the first element and first is set to false. For all subsequent elements in arr, if value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far. Choice III sets max to the first value in arr. Then it accesses each subsequent value in arr checking to see if the value is greater than max, if it is max is assigned this element since it is now the largest value so far.

In the first iteration of the binary search, it will check the value at index (0 + 7) / 2 which is index 3. Since 8 is greater than data[3], start is assigned mid + 1 which is 4 and the process will repeat. In the second iteration of the while loop, it will check the value at index (4 + 7) / 2 which is index 5. Since data[5] is 8, 5 is returned.

This recursive method starts at the end of the array numbers by setting numVals to numbers.length and checks to see if this element is the same as v, which is equal to the actual parameter val. If it is, it sets k to 1. The method recursively calls mystery, decrementing numVals by 1 each time. Once, numVals is equal to 1 the method checks to see if element 0 is equal to v and then the recursion is complete and k is returned. In each iteration, k will either be 1 or 0, based on whether the element is equal to v or not. The sum of all the values of k will be the return value of the original call to mystery.

The first for loop uses the set method to change the value of each element in students to “Alex”. When the set method is called, it returns the value that was originally at this index. So, the first loop will print Alex Bob Carl. At this point all elements have been set to “Alex”. The second for loop uses an enhanced for loop to access every element and will print Alex Alex Alex.
Missed Topics
-
Class Inheritance and Method Overriding: Explaining the behavior of classes A and B, where B inherits from A and overrides the show method.
-
Initialization and Variable Assignment: Discussing the importance of proper initialization, especially in the context of a variable like maxVal.
-
String Concatenation and Logical Errors: Addressing issues related to string concatenation leading to incorrect results in a method.
-
Nested Loops and Loop Control: Analyzing the behavior of nested loops, specifically understanding the relationship between the outer and inner loops.
-
Array Manipulation: Discussing how specific elements in an array are manipulated, including the calculation of values in a multi-dimensional array.
-
Logical Operators and Conditions: Pointing out logical errors in conditional statements, emphasizing the significance of proper use of logical operators.
-
Mathematical Operations: Involving understanding the result of mathematical operations, such as multiplication and division.
-
Recursion: Analyzing a recursive method and its behavior in a specific context, including the base case and return values.
-
Binary Search Algorithm: Explaining the mechanics of a binary search algorithm and identifying the return value.
-
Enhanced for Loop: Describing the behavior of an enhanced for loop when accessing elements in an array.
-
Attention to Detail: Recognizing the impact of details like the presence of the ‘!’ sign in a logical condition.