Main Binary Lesson

Binary
Objective:
To understand the basics of binary numbers, including their representation, conversion, and arithmetic.
What is Binary?
- Binary is a numeral system that uses only two digits, 0 and 1, to represent numbers, characters, and other data. It is also known as base-2 numeral system, which is in contrast to the decimal system, which uses ten digits (0-9) to represent numbers. In binary, each digit represents a power of 2, starting from the rightmost digit, which represents 2^0, and moving left, with each digit representing a power of 2 one greater than the previous digit.
What is it used for?
Binary is used in computing and digital communication systems because electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, work with digital signals that can only represent two states, on and off, or high and low. By using binary, computers can represent and process all kinds of data, including text, images, audio, and video.
Text
When you type a letter or character on your keyboard, the computer converts it into a binary code consisting of 0s and 1s. Each character is assigned a unique binary code using an encoding system such as ASCII . This binary code is stored in the computer’s memory or on a storage device, such as a hard drive or flash drive.
Image:
Digital images are made up of pixels, each of which is represented by a binary value. The binary code for each pixel determines its color and position in the image. The more pixels an image has, the more detailed and higher quality it will be.
Audio:
Digital audio files are also represented in binary format. The sound waves are sampled at regular intervals, and each sample is converted into a binary value using a process called quantization. The binary values are then stored as a digital audio file.
Video:
Digital video files are made up of a series of images or frames, each of which is stored as a binary file. Like digital images, each frame is made up of pixels that are represented by a binary value. The video file includes information on how each frame should be displayed and how they should transition from one to another.
What else does it represent?
In addition to representing numbers, binary is used to represent characters and other data in a system called ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange). Each character is represented by a unique combination of 8 binary digits, known as bits. For example, the capital letter A is represented by the binary code 01000001.
- 0 = represents OFF
- 1 = represents ON
Fun Fact! Connections with Binary

Do you see how the iconic power button is comprised of a zero and a one? The zero represents the device being off, and the one represents the device being on.
What is “0b”
In Python, you can specify a binary number by prefixing it with 0b. For example, 0b1010 represents the binary number 1010. The bin() function converts a decimal number to a binary string, while the int() function with base 2 as the second argument converts a binary string to a decimal number.
convert binary to decimal:
binary_num = '1010'
decimal_num = int(binary_num, 2)
print(decimal_num)
What is the code above doing? This code is converting a binary number represented as a string, ‘1010’, to a decimal number using the built-in Python function int(). The second argument, 2, tells int() to interpret the string as a binary number. The resulting decimal number, 10, is then stored in the variable decimal_num, and printed using the print() function.
convert decimal to binary:
decimal_num = 10
binary_num = bin(decimal_num)
print(binary_num)
What is the code above doing? This code is converting a decimal number, 10, to a binary number represented as a string using the built-in Python function bin(). The resulting binary number, ‘0b1010’, is then stored in the variable binary_num and printed using the print() function. So, the output of this code will be: 0b1010
Now that you kind of understand the concept, try to convert a string of letters into binary.
convert string to binary:
string = 'Hello World'
binary_string =
print(binary_string)
Binary Vocabulary
Bit= A binary digit = the minimum unit of binary information stored in a computer system (only two states: 1 or 0)
ex. 1 or 0
Nibble= 4 bits or half of a byte
ex. 0001
Byte= 8 bits or 2 nibbles
ex. 01110101
Boolean Expressions
A Boolean expression is a logical statement that is either TRUE or FALSE
- compare data to test if data is equal to, greater than, or less than other data
How is Binary Related to Boolean Expressions?
Binary and Boolean expressions are closely related because Boolean expressions are typically used to evaluate binary values, which can either be true or false (1 or 0).
Binary values are used to represent information. Boolean expressions are used to express the logical operations performed on these binary values(AND, OR, and NOT).
| Operator | Logical Operation |
|---|---|
| and | Conjunction |
| or | Disjunction |
| not | Negation |
Truth Tables
Truth tables represent the possible inputs and outputs of the logical operations of AND, OR, NOT, and XOR.
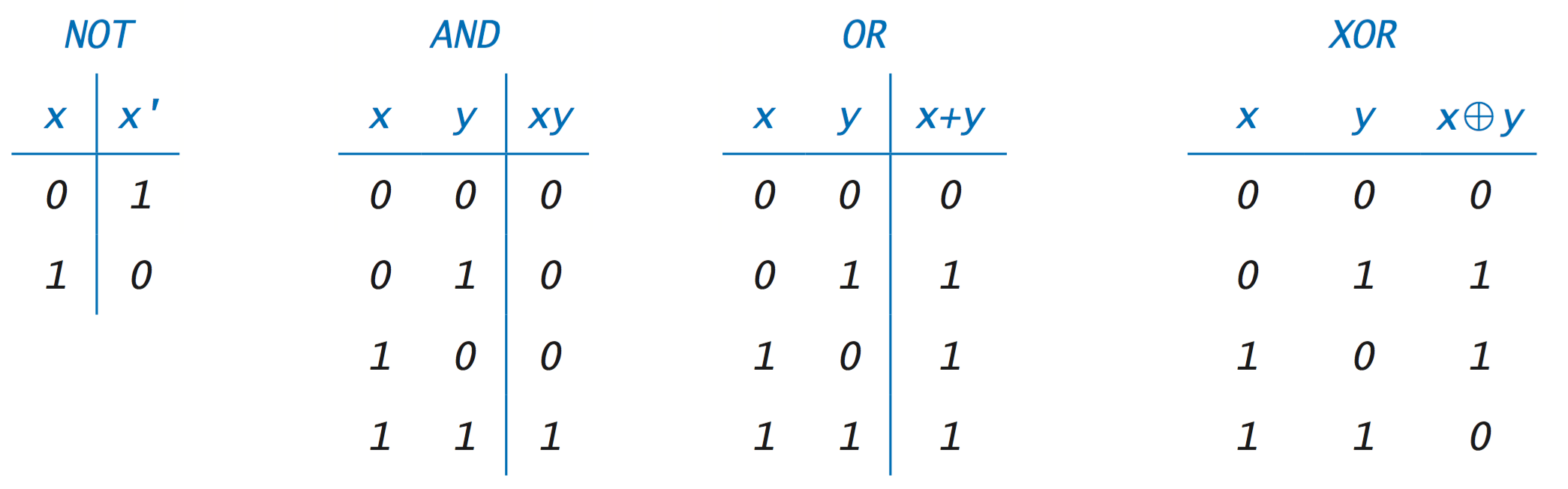
Examples:
AND:
5 > 3 and 5 == 3 + 2
true
5 < 3 and 5 == 5
false
OR:
5 == 5 or 5 != 5
True
5 < 3 or 5 != 5
False
What About a Real Life Example?
Here is an example of the use of boolean expressions in a real life situation.
age = 18
citizen = True
if age >= 18 and citizen:
print("You are eligible to vote.")
else:
print("You are not eligible to vote.")
You are eligible to vote.
Conversions with Binary
Converting Binary to Decimal
Since binary is a base two system, we can count in binary by using powers of two.

- Read from right to left.
- Each digit is the placeholder for a power of two. As you work your way left, you add one to the power of 2. For an example:

Above, you can see that you start with 20, then 21, 22 and so on.
- When you see the digit (bit) as a 1, it means that you are adding that power’s value to your “total” Look below for an example:
Make sure that you are starting with 20, NOT 21
ex.
20= 1, so:
0001 = 1
21= 2, so:
0010 = 2
22= 4, so:
0100 = 4
Now add them up!
0111 = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7
Now to convert decimal to binary simply reverse this process. lets take 7 for example
- picture
Now to convert decimal to binary simply reverse this process. lets take 7 for example
- picture
Converting decimal to Hexadecimal
- Now this is a little bit different then converting to binary
- Since hexademical is a base 16 number system and decimal is a base 10 number system.
- First you need to assigne each letter past 9 for hexademical as symbol all the way up to the number 15
- People ususally use letters although any symbol can work.
- picture
- picture
- Now to convert decimal to hexademical
-
picture
- Now this is a little bit different then converting to binary
- Since hexademical is a base 16 number system and decimal is a base 10 number system.
- First you need to assigne each letter past 9 for hexademical as symbol all the way up to the number 15
- People ususally use letters although any symbol can work.
- picture
Converting Binary to ASCII

You can play round with this tool to convert your text to binary and vise versa
Click Here to view a full conversion table between binary, hexadecimal, and ASCII
Binary Search
Binary search is an algorithm that helps find an item in a sorted list of items by dividing the list in half until the desired item is found. The binary search algorithm starts at the middle of a sorted data set of numbers and eliminates half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated.

- In this example, the target number is 7. Since 7 is greater than 2, the midpoint of the list, we now only search the higher side. When searching the higher side, 7 is still greater than the middle number so we search the higher side again until we reach the target number of 7.
Binary search is an efficient way to scan through larger arrays. A binary search is often more efficient than sequential/linear search when applied to sorted data. This is due to the greatest number of steps required following the format: log2(n)+1, in which n is the number of items in the array.
- For an example, an array with 10,000 items would only require a maximum of 14 steps (log2(10,000)+1 = 14) instead of 10,000 steps for a sequential/linear search. As lists grow larger, binary search can be a great help in decreasing program time and increasing efficiency.

- Binary search also works with a list of strings. We can sort them alphabetically and use the same method to find the desired string.
Activity Idea with students:
-
Write down a list of numbers (e.g., 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15) on a piece of paper or whiteboard.
-
Ask your partner to choose a number from the list (without telling you which one they chose).
-
Your partner will then try to guess your number using binary search. Begin by guessing the middle number in the list (in this case, 7).
-
Ask your partner whether their number is greater than, less than, or equal to your guess of 7.
-
Based on their response, eliminate either the left or right half of the list and repeat the process, guessing the middle number of the remaining half.
-
Continue this process of dividing the remaining numbers in half and guessing the middle number until you guess your partners number correctly.
-
For example, if your partner chose the number 9, the process might look like this:
- Guess 7
- says their number is greater than 7
- Eliminate the left half of the list (1, 3, 5, 7)
- Guess 11 (the middle number of the remaining half)
- says their number is less than 11
- Eliminate the right half of the remaining numbers (13, 15)
- Guess 9 (the middle number of the remaining half)
- says you guessed their number correctly!
Binary Search Trees
We can represent binary searches with binary search tree diagrams. These diagrams help represent the number of iterations required to find a desired item.

Hacks
STUDENTS: COMPLETE HACKS IN NOTEBOOK wget here: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/avac54765/fastpages-ava/master/_notebooks/2023-04-28-Binary-Lesson-Runtimeterror.ipynb
You will NOT be awarded any points for sections that are INCOMPLETE
- 10 conversion hax
Hacks Scoring
| Hack | Comments | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Note Taker | fill in the blanks above | 0.1 |
| Lesson Quiz | under 100% = 0.1 only | 0.2 |
| Binary Game | Must get to a score of 10 with screenshot | 0.2 |
| Binary Conversions Practice | if incorrect= 0.2 awarded | 0.2 |
| Binary Search Questions | if incorrect= 0.2 awarded | 0.2 |
| Extra Credit | MUST SHOW WORK | 0.1 |
| Total | expected= 0.9/1 | 1/1 |